In the quiet shadows of an abandoned house, a tale unfolds—a story of neglect, resilience, and the transformative power of compassion. This is the narrative of a girl whose warm hug became the beacon of hope for a dog left to starve and suffer in isolation. The poignant rescue not only warmed the dog’s cold heart but also stirred a collective wave of sadness and sympathy.
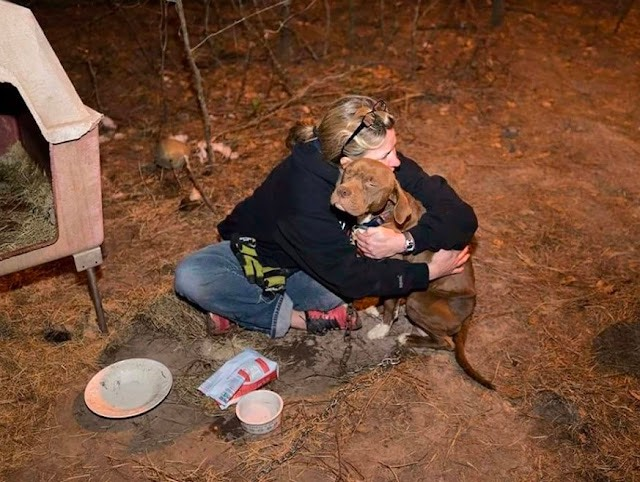

The story begins in the desolation of an abandoned house, where the echoes of neglect reverberate through the silent corridors. In a dark corner, a dog, once a beacon of joy, now endures days of hunger and loneliness, the weight of abandonment etched in the weariness of its eyes.
Enter the girl, a compassionate soul who, moved by empathy, discovers the forsaken canine. Ignoring the dilapidated surroundings, she extends a hand of rescue to the starved creature, embodying the essence of kindness that transcends species boundaries.
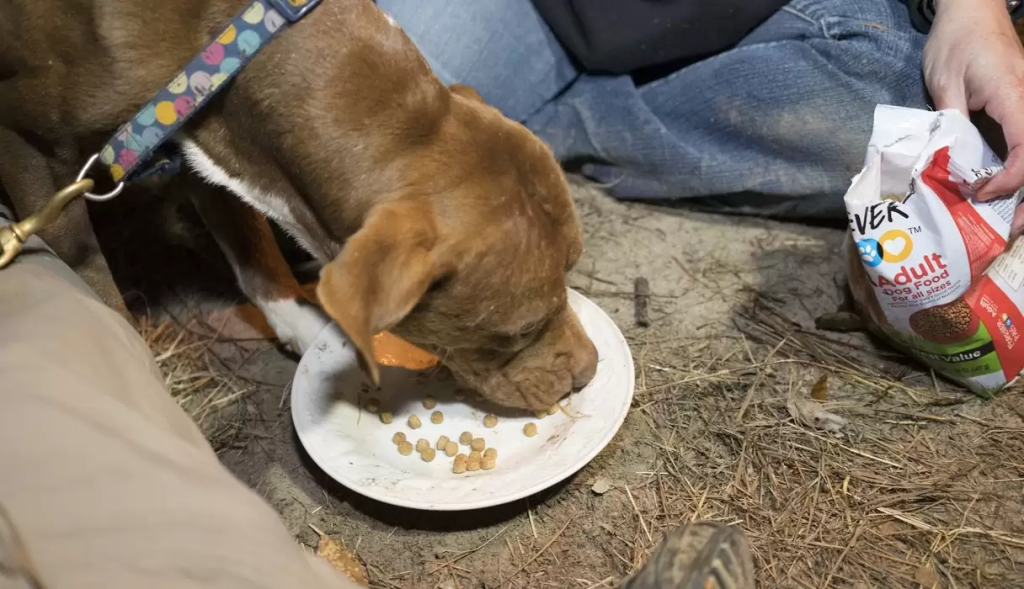

As the girl wraps the emaciated dog in a blanket of compassion, a warmth permeates the air—an embrace that speaks volumes without words. The once-neglected creature, now cradled in the arms of care, begins to feel the thawing of its heart, and a flicker of life returns to its dimming eyes.
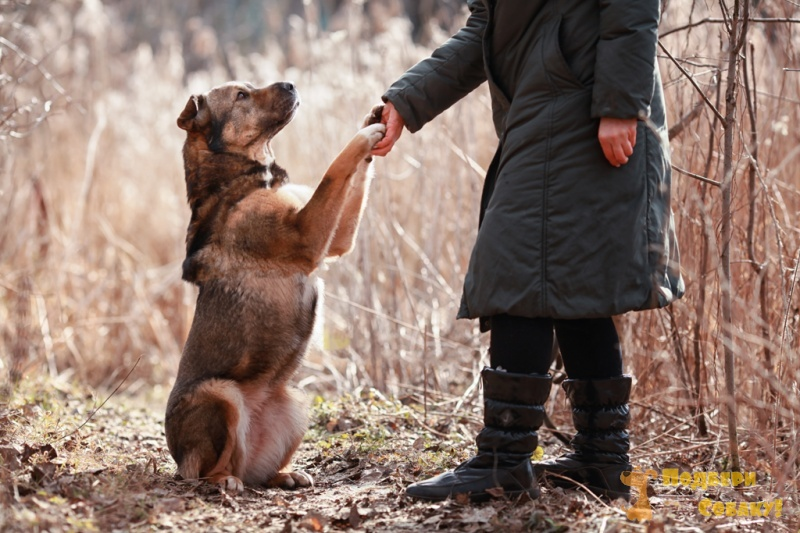

The pivotal moment comes when the girl, recognizing the power of touch, envelops the dog in a warm hug. It is a gesture that transcends the physical, conveying a sense of solace and understanding that words could never capture. In that embrace, a connection is forged—a bridge between two souls, one yearning for love, the other offering it unconditionally.
The heartwarming rescue, shared through the lens of compassion, resonates with the broader community. As the images and story circulate, they evoke a collective sadness, inviting onlookers to confront the harsh realities of animal abandonment and rally against such acts of neglect.
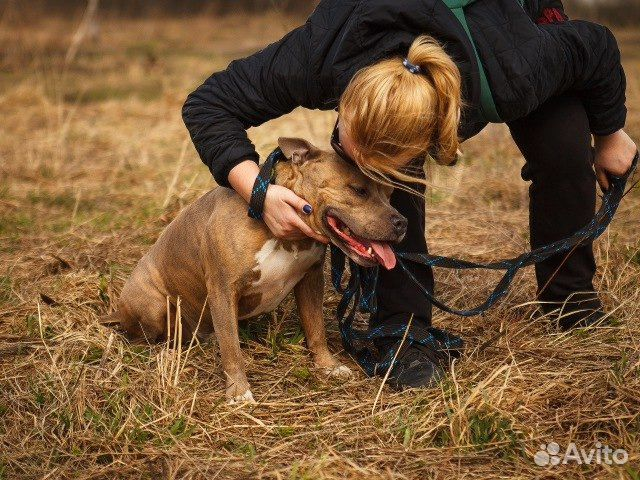

In conclusion, the story of the girl’s warm hug rescuing the abandoned and starved dog is a testament to the redemptive power of compassion. It serves as a call to action against the silent suffering of neglected animals, encouraging a collective effort to create a world where every creature, no matter how forsaken, can experience the warmth of love and care. The narrative is a poignant reminder that, in the embrace of compassion, even the most desolate souls can find healing, redemption, and a chance for a brighter tomorrow.
15 Things Moms Do That Make Them Even More Incredible
Each pregnancy alters your body irrevocably. And we don’t mean the stretch marks or the scars. We mean the forever-changed DNA. Ask any new mother and she’ll list out a litany of things that are now different for her. Like a forgetful mommy brain that, according to science, makes the mother-child bond stronger.
We at Bright Side salute all moms and believe that they are real-life superheroes. To honor all mothers, we found some mommy facts proving there’s nothing like a mother’s love. Or the science behind it.
1. Motherhood changes you, and your DNA.
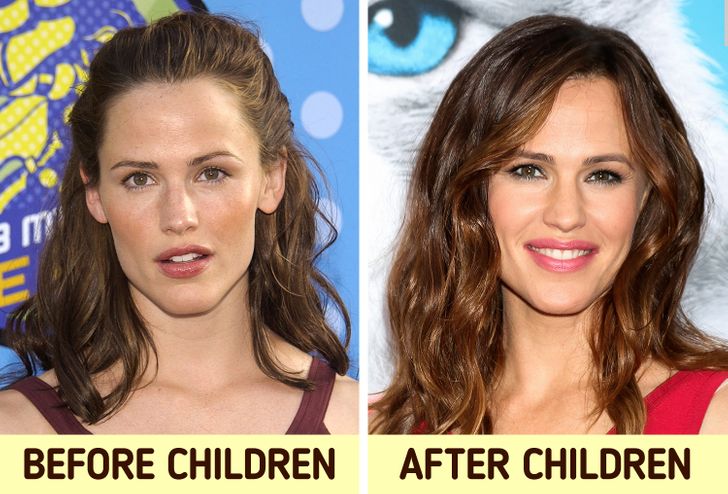

A chimera is a legendary beast made of different animals. And we are likening mothers to chimeras because every child that a mother carries leaves their DNA inside her. Basically, fetal cells enter a mother’s bloodstream and stay in her body forever. Researchers allege that these cells can affect the mother both positively and negatively. On one hand, it can speed up healing but on the flip side, it can increase the risk of cancer.
So when they say motherhood changes you, it does so at an elemental level as well. Jennifer Garner’s stunning countenance reflects just that.
2. The baby can taste what their mother eats.

Studies show that what a mother eats flavors the amniotic fluid. Something a baby gulps down several times a day. Basically, a baby can taste what their mother eats from within the womb.
A study showed that infants whose mothers ate carrots while pregnant seemed to enjoy cereal prepared with carrot juice more than others. So if you want to develop your baby’s palate for healthy, crunchy veggies, chow down on them while you are pregnant.
3. Kissing babies is more “healing” than we think.

Any new mom will tell you that the urge to kiss a newborn is intense. It’s innate and biological in nature. And science says that when mothers kiss their babies, it’s not just love, it’s medicine.
A mother’s body samples the pathogens found on the baby’s face, and more magic happens within her own body. Especially to her breastmilk, the main source of nutrition and immunity for the baby.
4. Pregnant women make enormous amounts of estrogen.

Pregnancy sends a woman’s body into overdrive. The uterus expands to 500 times its normal size and then shrinks back after birth. The blood volume increases and to tackle that, the heart expands a little too.
And it’s not just this, a woman makes more estrogen in a single pregnancy than she would in her whole lifetime if she never got pregnant. There’s a reason why women are exhausted when expecting and need sleep and rest for a healthy delivery and recovery.
5. A mother’s smile is near magical.
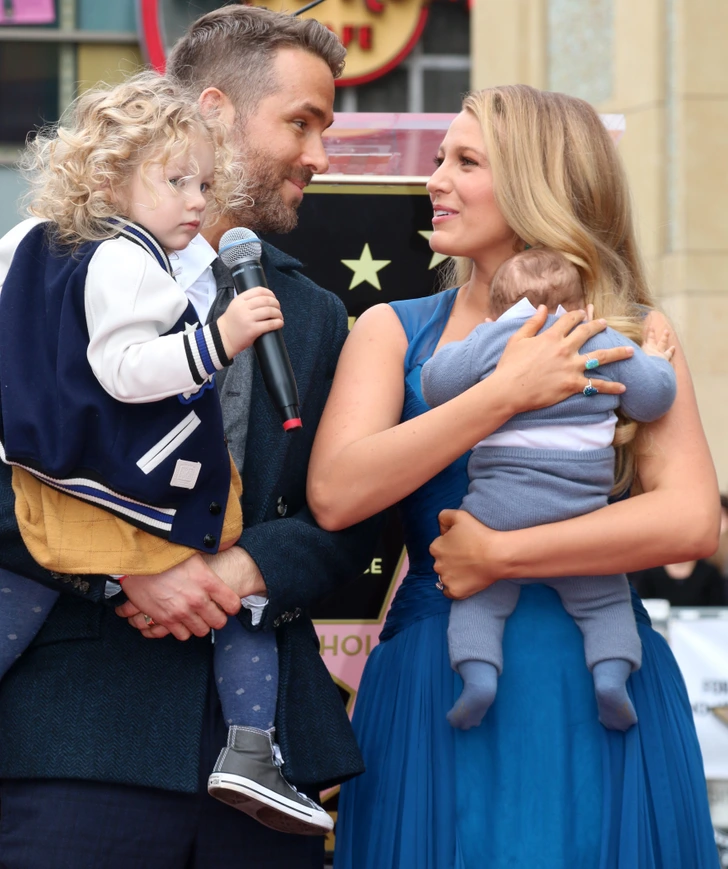

Moms are near magic, and so is their smile or affection. While you need your mother at all ages, it’s the helpless infant who is most dependent on their mom.
Studies show that when mothers smile, coo, and show affection to their babies, their heartbeats synchronize into the same beat. So if a baby is distressed, it calms them down. This is the reason why newborns need mothers the most when they are fussy and refuse to be calmed down by other family members.
6. Carrying boys can make you more nauseous.
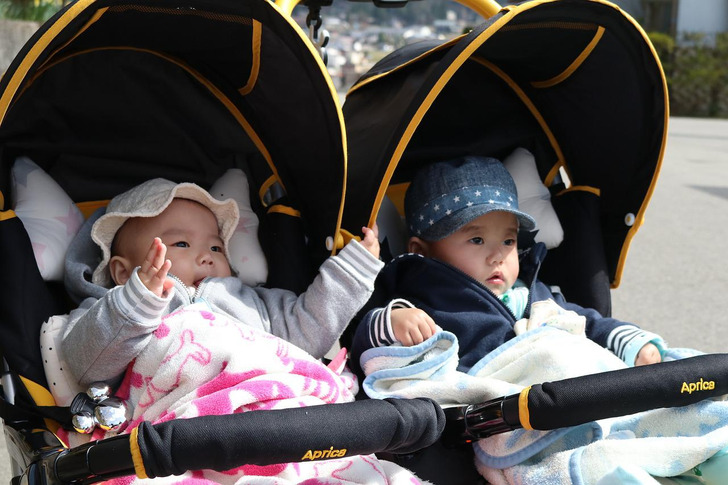

There’s a reason why little boys are made of “snips and snails and puppy dog tails” or so goes the nursery rhyme. This is because mothers who carry boys are more likely to be nauseous in the first and second trimesters, a study shows.
This is not to say that women expecting girls cannot have morning sickness or that all women who carry boys have more nausea. It’s just that if you are expecting a boy, chances are you may experience more nausea or food aversions.
7. Babies name their mamas.
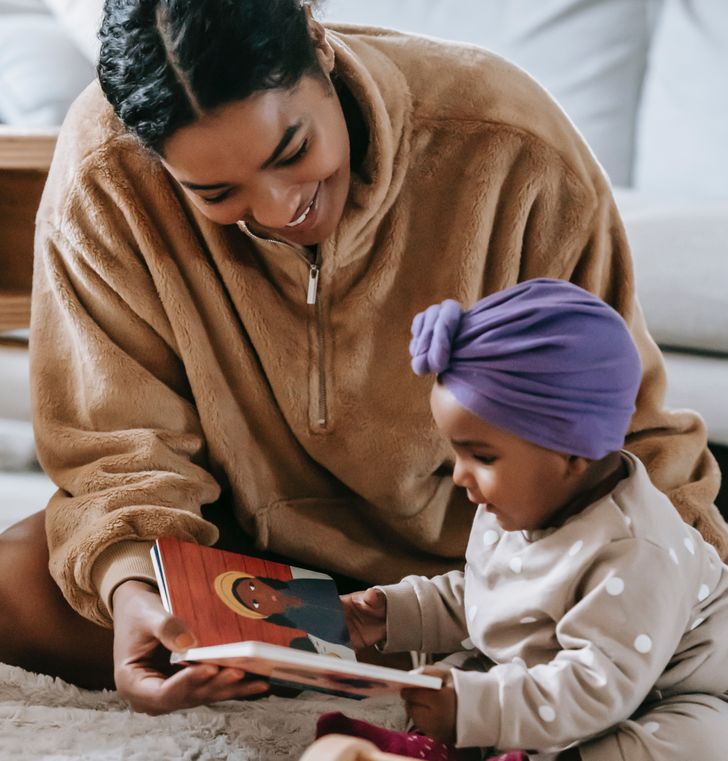

“Mom, mama, mummy, mamma, ammi, ma, me, emi, mimi.” There’s a pattern in the name for mother in all languages and this is because the “em” sounds are usually the first vocalization for a baby. It’s also the easiest sound a baby can make while babbling. And so it’s our babies who name us and call us mamas.
8. The mommy brain fog is very real.
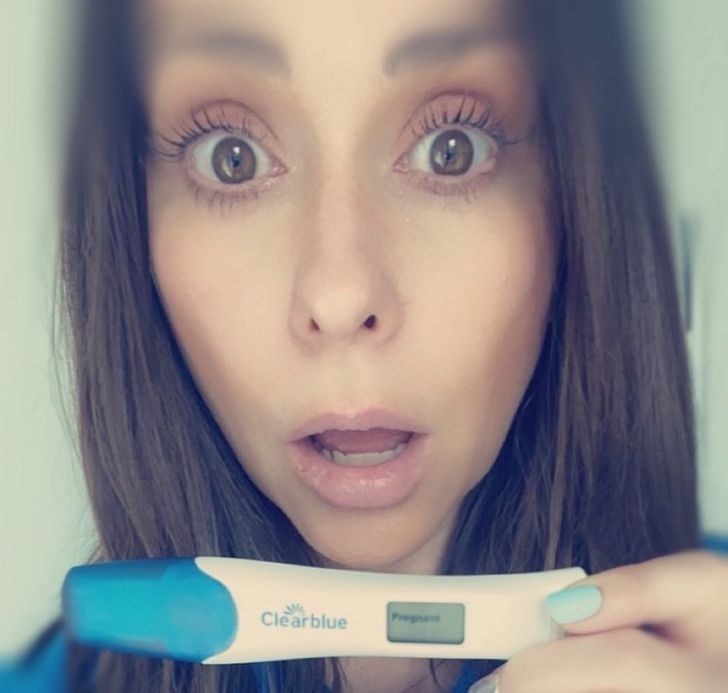
If you see new moms looking lost, there’s a scientific reason for this. Each pregnancy affects a woman’s brain and makes her lose gray matter. The effects last for around 2 years. Science says that this temporary bewilderment makes mothers closer to their babies as well.
That said, the gray matter regenerates and any confusion or forgetfulness is passing. The bond between a mother and her child is permanent.
9. A mother’s voice is as soothing as a hug.
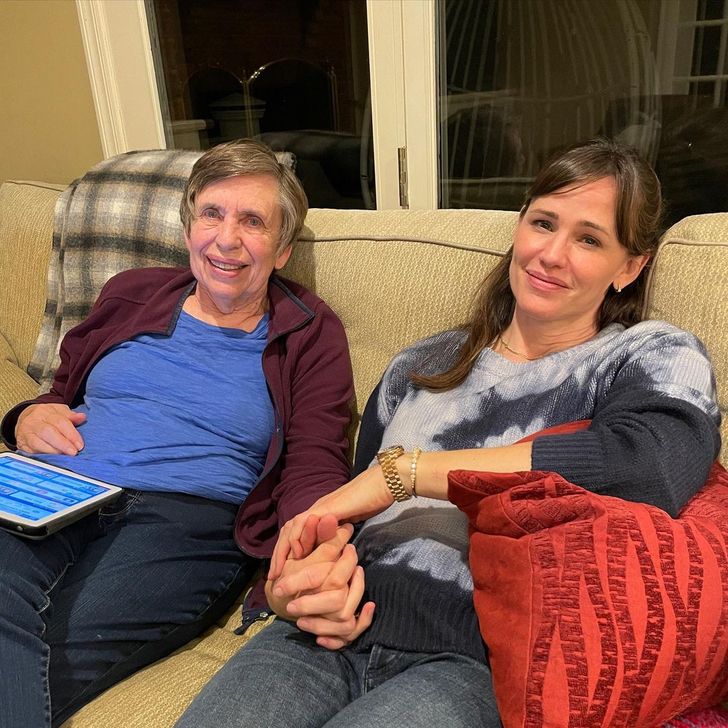

A study has shown that a mother’s voice, even on the telephone, is as calming as a hug. Researchers introduced stress to a group of girls and then had 1/3 of them hug their mothers, another 1/3 of them talk to their mothers, and 1/3 watched an emotionally neutral film. The girls who spoke to their mothers calmed down much faster, just like those who hugged.
This proves that if you are under stress, your mother’s voice can flood oxytocin into your bloodstream, making you feel better. And we think Jennifer Garner already knows that, pictured here with her mother.
10. Babies can cry in the womb.
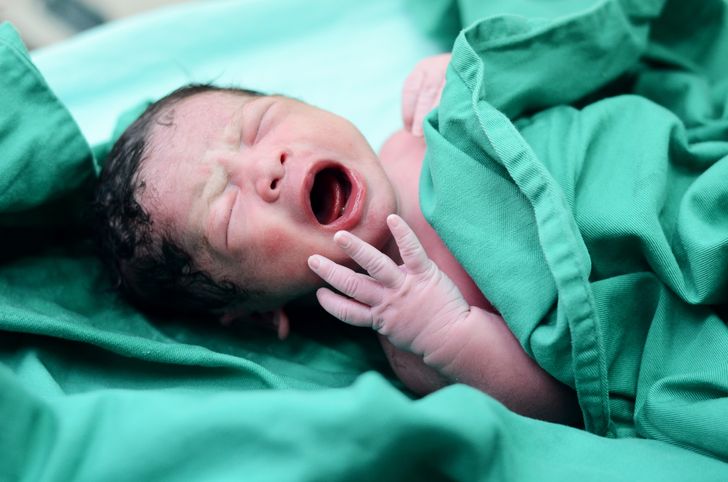
The baby’s first cry is not post-birth, rather studies now show that they can express displeasure inside the womb. This can happen as early as 28 weeks gestation.
Researchers played low-decibel sounds on the mother’s belly and could see that the baby opened their mouth and exhibited crying-like behavior. But it’s a silent cry. Researchers also added that this in-vitro crying was nothing the mother should worry about.
11. Pregnancies leave women vulnerable to tooth decay.
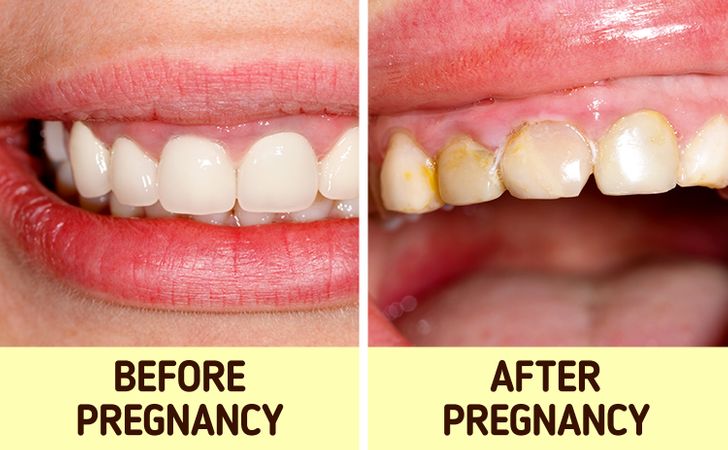
Pregnant women are at risk for tooth decay and there are many reasons why. The changes in diet due to cravings may give some women a sweet tooth and the hormones that cause nausea, meaning more acidity on your mouth, to mention a few. This leads to gum disease and decay.
A simple way to prevent it all is by making oral health a priority, especially when you are pregnant.
12. The earliest milk bottle use came to be 7,000 years ago.
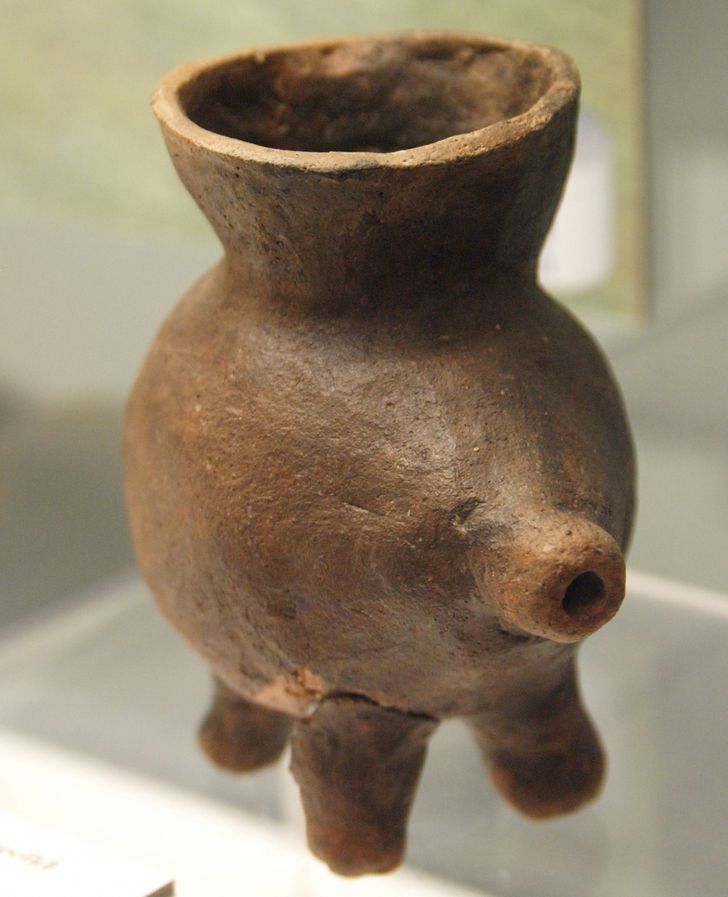

As it turns out, the breast/bottle debate is prehistoric. And mamas back then were pretty innovative too. Researchers have found little clay vessels, some shaped into mythical animals with hands and feet, with milk residue in them.
The earliest of them date back to 7,000 years ago and have been identified as prehistoric feeding bottles for babies. The dairy residue has been identified as breastmilk and milk from a cow, sheep, or goat.
13. The Ice Age made human breast milk more nutritious.
Human beings need sunlight to survive because our bodies only synthesize vitamin D in the sun. Allegedly, the last Ice Age should have wiped us out because newborns were not getting any vitamin D, considering the intense cold and lack of sunshine.
Scientists believe that a genetic tweak happened and mothers could transmit vitamin D and essential fatty acids to their newborn babies, and this may have ensured human survival.
14. Pregnancies can be contagious.
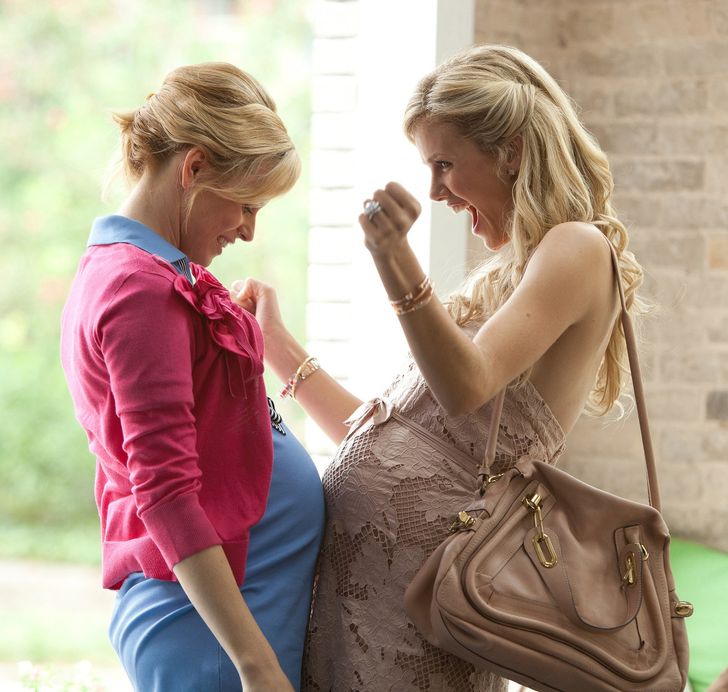

A study of more than 30,000 women conducted in Germany has indicated that pregnancy is contagious. It spreads from woman to woman in workplaces, in an endearing way. The results stated that “in the year after a colleague gives birth, transition rates to first pregnancies double.”
So if you are in the workplace and someone is pregnant, expect more pregnancies to pop up.
15. Most mammal moms carry their babies on the left.
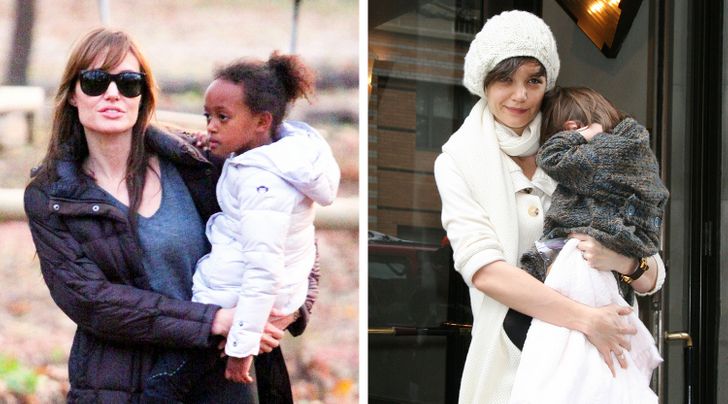

Human mothers and even some mammal mamas cradle their babies on the left side of their bodies, closer to their heart. This is irrespective of a left-handed or right-handed mom. Science says that all the sensory information that comes from the left side of the body is processed on the right side of the brain.
The right side is where all the emotions are. And surprisingly enough, babies prefer to keep their moms on their left side as well, so it works for both mom and babe.
Bonus: Celebrity moms speak about motherhood.
Rosie Huntington-Whiteley
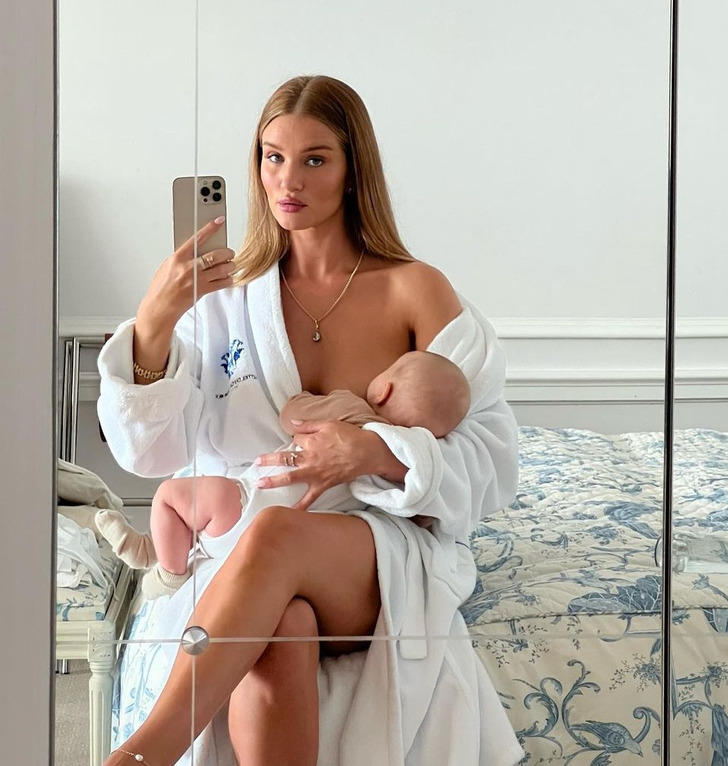

“I did start to feel this new sense of life. And now my confidence is so much greater.”
Lauren Burnham Luyendyk
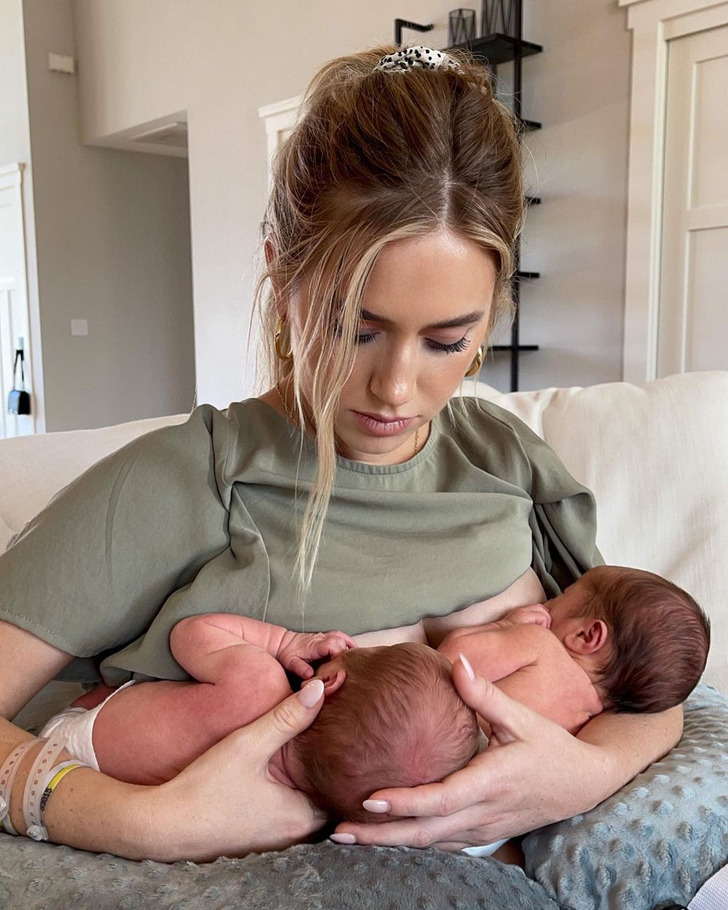

“Breastfeeding is one of the hardest things I’ve ever done. I’m in awe of the ladies that make it look so effortless, and even the ones who don’t, you are superheroes.”
Do you have any other experiences as a child or a mother that show us that moms are actual superhumans? Share your motherhood stories with us and spread the joy.
Please note: This article was updated in June 2022 to correct source material and factual inaccuracies.
Preview photo credit laurenluyendyk / Instagram



Leave a Reply